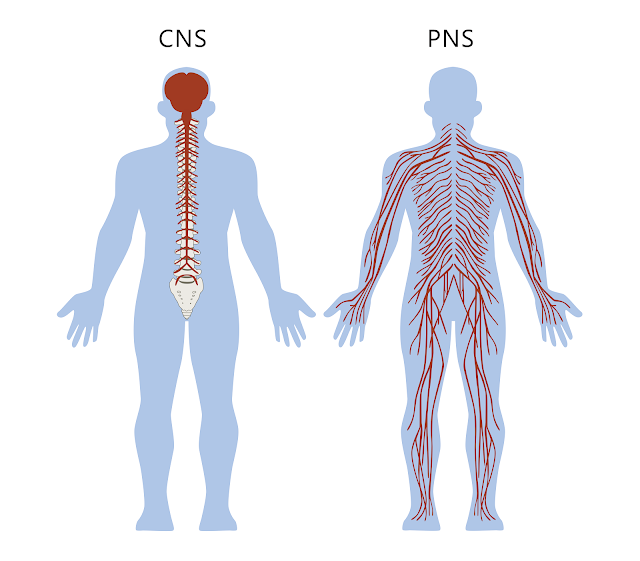
The nervous system.
Brain. Spinal Code and complex network of nerves.
The Human brain is a complex organ.
In bilaterian animals, which make up the great majority of existing species,
the nervous system has a common structure that originated early in the Ediacaran period,
over 550 million years ago.
Nerves are like cables.
also read this
The Divisions of Brain
There are three major regions in the brain of humans and other vertebrates. These are forebrain, midbrain, and hindbrain. Important parts of each of these regions
are described below:
Forebrain
Forebrain is the largest area of the brain. It is most highly developed in humans.
The following are the important parts of this region.
(i) Cerebrum is the largest part of the forebrain. It controls skeletal muscles, thinking, intelligence, and emotions. It is divided into two cerebral hemispheres. The anterior parts of cerebral hemispheres are called olfactory bulbs which receive impulses from olfactory nerves and create the sensation of smell. The upper layer of cerebral hemispheres i.e. cerebral cortex consists of grey matter. The grey matter of the nervous system consists of cell bodies and non-myelinated axons. Beneath this layer is present white matter. The white matter of the nervous system consists of myelinated axons. The cerebral cortex has a large surface area and is folded in order to fit in the skull.
It is divided into four lobes.
1. Frontal Lob motor functions, permits conscious control of skeletal muscles and coordinates movements involves in speech.
2. Parietal lob Contains sensory areas that receive impulses from the skin.
3. Occipital lob Receives and analyzes visual information
4. Temporal lob Concerned with hearing and smell.
(ii) Thalamus lies just below the cerebrum. It serves as a relay center between various parts of the brain and the spinal cord. It also receives and modifies sensory impulses (except the nose) before they travel to the cerebrum. Thalamus is also involved in pain perception and consciousness (sleep and awakening).
(iii) Hypothalamus lies above the midbrain and just below the thalamus. In humans, it is roughly the size of an almond. One of the most important functions of the hypothalamus is to link the nervous system and the endocrine system. It controls the secretions of the pituitary gland. It also controls feelings such as rage, pain, pleasure, and sorrow.
(iv)Hippocampus is a structure that is deep in the cerebrum. It functions for the formation of new memories. People with a damaged hippocampus cannot remember things that occurred after the damage but can remember things that had occurred before the damage.
Midbrain
The midbrain lies between the hindbrain and the forebrain and connects the two. It receives sensory information and sends it to the appropriate part of the forebrain. Midbrain also controls some auditory reflexes and posture. It is also a collaborator of the spinal cord with the fore-brain.
Hindbrain
Hindbrain consists of three major parts.
(i) Medulla oblongata lies on the top of the spinal cord. It controls breathing, heart rate, and blood pressure. It also controls many reflexes such as vomiting, coughing, sneezing, etc. Information that passes between the spinal cord and the rest of the brain passes through the medulla.
(ii) Cerebellum is behind the medulla. It coordinates muscle movements.
(iii) Pons is present on top of the medulla. It assists the medulla in controlling breathing. It also serves as a connection between the cerebellum and the spinal cord.
- Spinal Cord
The spinal cord is in fact a tubular bundle of nerves. It starts from the brain stem and extends to the lower back. Like the brain, the spinal cord is also covered by the meninges. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord.
The outer region of the spinal cord is made of white matter (containing myelinated axons). The central region is butterfly shaped that surrounds the central canal. It is made of grey matter (containing neuron cell bodies).
31 pairs of spinal nerves arise along the spinal cord. These are “mixed” nerves because each contains axons of both sensory and motor neurons.
The spinal cord performs two main functions:
1. It serves as a link between body parts and the brain. The spinal cord transmits nerve impulses from body parts to the brain and from the brain to body parts.
2. Spinal cord also acts as a coordinator, responsible for some simple reflexes.
The spinal cord is roughly 40cm long and about as wide as
your thumb for most of its length.
Peripheral Nervous System
The cranial and spinal nerves make two pathways.
a Sensory pathway (conducting impulses from receptors to CNS)
b. Motor pathway (conducting impulses from CNS to effectors).
The Motor pathway makes two systems.
a.Somatic Nervous System b.Autonomic Nervous System
Somatic Nervous System
It is responsible for conscious and voluntary actions. It includes all of the motor neurons that conduct impulses from the CNS to skeletal muscles.
Autonomic Nervous System
It is responsible for the activities, which are not under conscious control. It consists of motor neurons that send impulses to cardiac muscles, smooth muscles,s, and glands. The autonomic nervous system comprises the sympathetic system and parasympathetic system. The sympathetic nervous system prepares the body to deal with emergency situations. This is often called the “fight or flight” response. During an emergency situation, this system takes necessary actions. For example; it dilates pupils, accelerates heartbeat, increases breathing rate, and inhibits digestion. When stress ends, the parasympathetic nervous system takes action and normalizes all its functions. It causes pupils to contract, promotes digestion, and slows the rate of heartbeat and breathing rate.
Neuron.
Reflex Action
When the central nervous system sends impulses to muscles and glands, two types of actions (responses) result.
1. The higher centers of the brain control conscious action or voluntary actions.
2. When impulses are not passed to the higher centers of the brain, it results in responses that are not under conscious control. Such responses are called involuntary actions. Sometimes, the involuntary response produced by the CNS is very quick. Such a response is called reflex action. The pathway followed by the nerve impulses for producing a reflex action is called the reflex arc. The most common example of reflex action is the withdrawal of the hand after touching a hot object. In this reflex action, the spinal cord acts as the coordinator. Heat stimulates temperature and pain receptors in the skin. A nerve impulse is generated which is carried by sensory neurons to the interneurons of the spinal cord.
 |
| reflex action. |
Nerves.
A type of cell that receives and sends messages from the body to the brain and back to the body.
Receptors.
We know that the organs or parts which are specifically built to detect particular types of stimuli are
called sense organs or receptors. The main receptors in man are eyes, ears, nose, taste buds, receptors
of touch, heat and cold, etc.
M.A F SALEEM.
Two ways to have a healthy brain good diet and exercise.
Two ways to have a healthy brain good diet and exercise.
Two ways to have a healthy brain good diet and exercise.
.