|
| human ear |
- The external or outer ear consists of Pinna or auricle.
- This is the outside part of the ear.
- Tympanic membrane (eardrum).
- The tympanic membrane divides the external ear from the middle ear.
- Middle ear (tympanic cavity), consisting of Ossicles.
- The inner ear consists of Cochlea.
Ear Hearing is as important as vision. Our ear helps us in hearing and also to maintain the balance or equilibrium of our body. The ear has three main parts i.e. external ear, middle ear, and internal ear.
 |
| human ear |
Parts of the Human Ear.
The three main parts of the human ear include the outer ear, middle ear, and inner ear.
External Ear.
The external Ear consists of the pinna, auditory canal, and ear drum (tympanum). Pinna is the broad external part, made of cartilage and covered with skin. It helps to direct sound waves into the auditory canal. There are special glands in the walls of the auditory canal, which produce wax. The wax and the hairs in the auditory canal protect the ear from small insects, germs, and dust. In addition to this, they help to maintain the temperature and dampness of the auditory canal. The auditory canal ends in the eardrum. This thin membrane separates the external ear from the middle ear.
Middle Ear Middle.
Middle Ear Middle ear is a chamber after the external ear. Three small bones, called middle ear ossicles, are present in a chain in the middle ear. These movable bones include the malleus, incus, and stapes. Malleus is attached to the ear drum, then comes the incus, and finally stapes that is connected with a membrane called an oval window. The oval window separates the middle ear from the inner ear. The middle ear also communicates with the nasal cavity through the Eustachian tube. This tube regulates the air pressure on both sides of the eardrum
Stapes are the smallest bone of the human body.
Inner Ear.
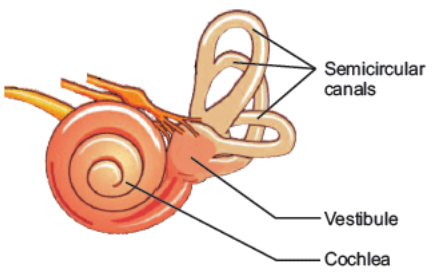
Inner Ear Inner ear consists of three parts i.e. vestibule, semicircular canals, and cochlea. The vestibule is present in the center of the inner ear. Three canals called semicircular canals are posterior to the vestibule. The cochlea is made of three ducts and wraps itself into a coiled tube. Sound receptor cells are present within the middle duct of the cochlea.
The Process of Hearing.
The pinna of the external ear focuses and directs sound waves into the auditory canal. The sound waves strike the eardrum and produce vibrations in it. From the eardrum, the vibrations strike the middle ear and produce further vibrations in the malleus, incus, and stapes. From stapes, the vibrations strike the oval window and then reach the fluid-filled middle duct of the cochlea. The fluid of the cochlea is moved and receptor cells are stimulated. The receptor cells generate a nerve impulse, which travels to the brain and is interpreted as sound.
For example, light travels faster than sound.
Lightning is caused by an electrical charge due to the movement of water droplets or crystals carried by the wind. The sudden increase in pressure and temperature from lightning produces rapid expansion of the air. This expansion of air produces a sound of thunder. The flash of lightning is followed after some seconds by a roar of thunder. This time difference is due to the fact that sound travels slower than light.
The Process of Hearing.
The pinna of the external ear focuses and directs sound waves into the auditory canal. The sound waves strike the eardrum and produce vibrations in it. From the eardrum, the vibrations strike the middle ear and produce further vibrations in the malleus, incus, and stapes. From stapes, the vibrations strike the oval window and then reach the fluid-filled middle duct of the cochlea. The fluid of the cochlea is moved and receptor cells are stimulated. The receptor cells generate a nerve impulse, which travels to the brain and is interpreted as sound.
Disorder of Ear.Deafness
Deafness is a state in which hearing is not possible. The defect of the eardrum, cochlea, middle ear ossicles, or auditory nerve may cause deafness. Infection in The eustachian tube may spread to the middle ear too. Eardrum may be damaged by an infection in the auditory canal. Excessive noise, strong blows on the cheek, pointed objects entering the auditory canal, and attacks from insects may also affect hearing.